The United States the National Security Agency (NSA) and Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) have taken the unusual step of publishing a joint security alert containing details about a new strain of Linux malware that the agencies claim was developed and deployed in attacks by Russian military hackers.
Through their joint alert, the two agencies hoped to raise awareness in both the US private and public sectors so IT managers could quickly deploy detection rules and prevention measures.
Based on evidence collected by the two agencies they announced that Russian hackers had introduced malware, named Drovorub, to place backdoors in hacked networks. FBI and NSA officials claimed the malware was the work of APT28 (Fancy Bear, Sednit), a codename given to the hackers operating out of military unit 26165 of the Russian General Staff Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU), the 85th Main Special Service Center (GTsSS).
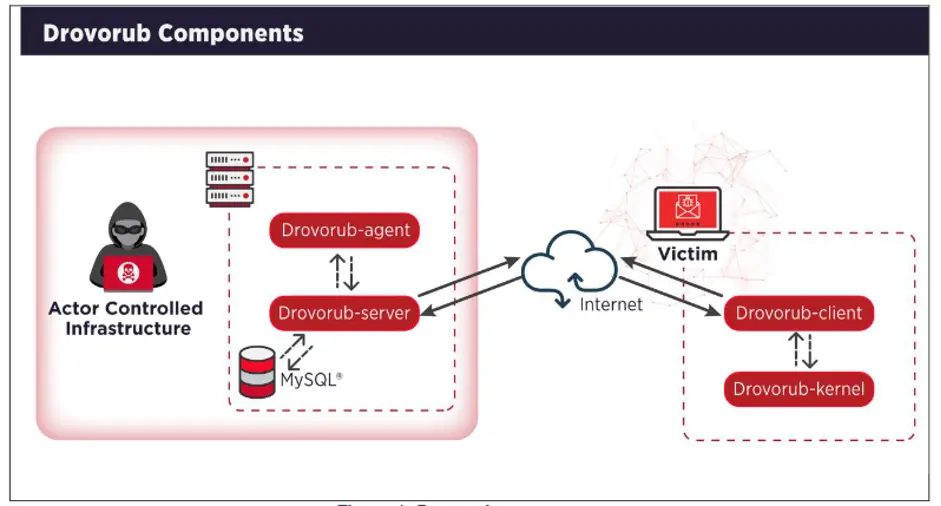
The two agencies stated that Drovorub is a multi-component system that comes with an implant, a kernel module rootkit, a file transfer tool, a port-forwarding module, and a command-and-control (C2) server. McAfee CTO, Steve Grobham said, “Drovorub is a ‘swiss-army knife’ of capabilities that allows the attacker to perform many different functions, such as stealing files and remote controlling the victim’s computer. In addition to Drovorub’s multiple capabilities, it is designed for stealth by utilizing advanced ‘rootkit’ technologies that make detection difficult. The element of stealth allows the operatives to implant the malware in many different types of targets, enabling an attack at any time.”
The United States has always been a target for potential cyber-attacks because of the large concentration of tech industries. The objectives of Drovorub were not explained in the report, but it is believed they could range from industrial espionage to election interference.
The technical and specification details released by the NSA and FBI on APT28’s Drovorub toolset are extremely useful to cyber defenders across the United States as this enabled joint defensive preparation.
. To prevent attacks, the agencies advised US organizations to update any Linux systems to a version running kernel version 3.7 or later. This would enable kernel signing enforcement, a security feature that would block APT28 hackers from installing Drovorub’s rootkit.
The joint security alert contained guidance for running Volatility; a probing for file hiding behavior, Snort rules, and Yara rules. Volatility is an essential tool to deploy proper detection measures.
Drovorub is the original name for the malware assigned by APT28 hackers, and not assigned by the NSA or FBI. It means chopped wood, from дрово, meaning “firewood”, and руб, the verb “to chop”. The FBI and NSA said they were able to irrefutably link Drovorub to APT28 after Russian hackers reused servers from different operational strings. The agencies claimed Drovorub connected via a known C&C server that was previously identified by Microsoft from APT28 operations targeting Internet devices in the spring of 2019.







